- (+91) 44223 92820
- (+91) 89036 01585
- info@saishanbusiness.in
SAP Support
- Functional Support on configuration
- System maintenance and upgrades
- Performance tuning and migrations
- ABAP and Interfaces
- Code review and standardization in custom development
- Transport management system
- Month end process and generation of Financial Statement version
- Monitor system health
- Build and monitoring dashboard through Solution Manager
- Root cause analysis and recommendation to pre-empt issues
User Acceptance Testing
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT) is the final phase of testing before an SAP system goes live, carried out by end users to validate whether the system meets business requirements and supports real-life scenarios.
- Test planning and case designs are based on business processes. Issues are tracked for fixing, and once resolved, testing is repeated.
- Data migration poses major challenges during UAT. Activities include data cleansing, removing duplicates, eliminating redundant information, and mapping essential data to SAP-defined searchable fields.
- UAT is performed whenever a new process is introduced into the system, aligned with SAP’s best business practices.
- To speed up and improve the quality of SAP UAT, it is essential to adopt advanced automation strategies.
- Test automation plays a crucial role in continuous testing by reducing manual workload and allowing more focus on designing effective test cases.
- Popular automated testing tools include Selenium, TestComplete, and Ranorex.
SAP Training
Normally training are provided to the end users at the time prior to Go Live. Most of the users may not be so familiar at that time when they attend the training initially. Even SAP system itself is very new to them. While using it in real time only they face quite lot of issues. To seek clarification at such time or to get additional information to be filled in the transaction, they may face issues. More over quite good number of human resource turnouts may be there. As such it is advised to keep SAP training as a continuous process for the defined business scenarios at regular intervals.
SAP Process Audit
Functional
In the functional side we identify the business processes relating to Core and Support businesses. Upon identification of processes, we ensure that strong inbuilt internal control system is available in the said processes. Mapping of such control system in the SAP defined Best Business Practices will be checked thoroughly.Technical
In the technical front, we verify the integration points of SAP between different modules. Main integration points are depicited below:- Unless and otherwise the accounts mapped to these points are verified at regular interval based on the business practices and user interaction, it could lead to error in valuation of inventory and the production order. Business decision taken on improper valuation could lead to major consequences.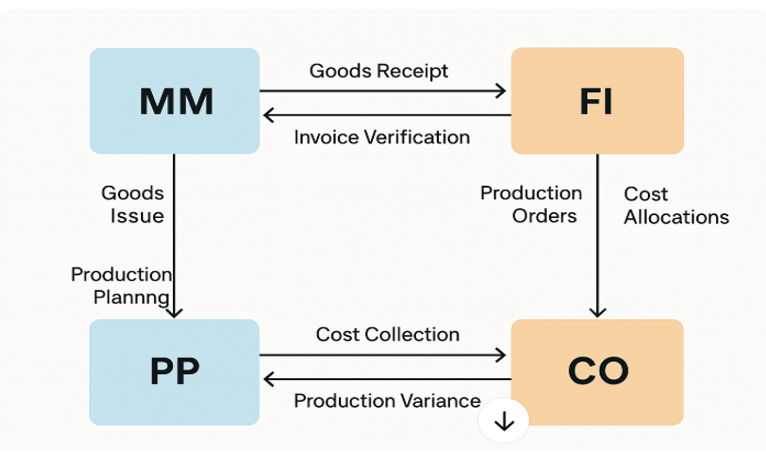
Integration Between SAP MM, PP, CO, and FI
End-to-End Integration at High Level
- MM: Raw materials purchased → Goods Receipt posted → Inventory increased in FI
- PP: Production order created → Raw materials issued (MM) → Costs collected (CO)
- PP: Production confirmed → Labor/machine time posted to CO
- PP: Finished goods received → Inventory value updated in FI
- CO: Order settled → Variances posted to FI GL accounts
- FI: Full financial trail available for audit/reporting
